Logging into the WordPress Admin Area
By default, all WordPress sites provide a URL in which to access the admin area of your site:
https://yoursite.com/wp-admin/
Technically, all users of a WordPress site, regardless of their user role, can login to the WordPress admin area. However, the permissions (or, what they have access to) varies depending on their role.
Administrators, for example, have access to everything in the admin area. They can make changes to every aspect of a WordPress site. Subscribers, on the other hand, only have access to one page—their profile. They can only update some personal information about themselves, and change their password; nothing else.
Admin Area Overview
First, let’s get acquainted with the 3 main areas that you’ll see on all pages within the WordPress admin area.
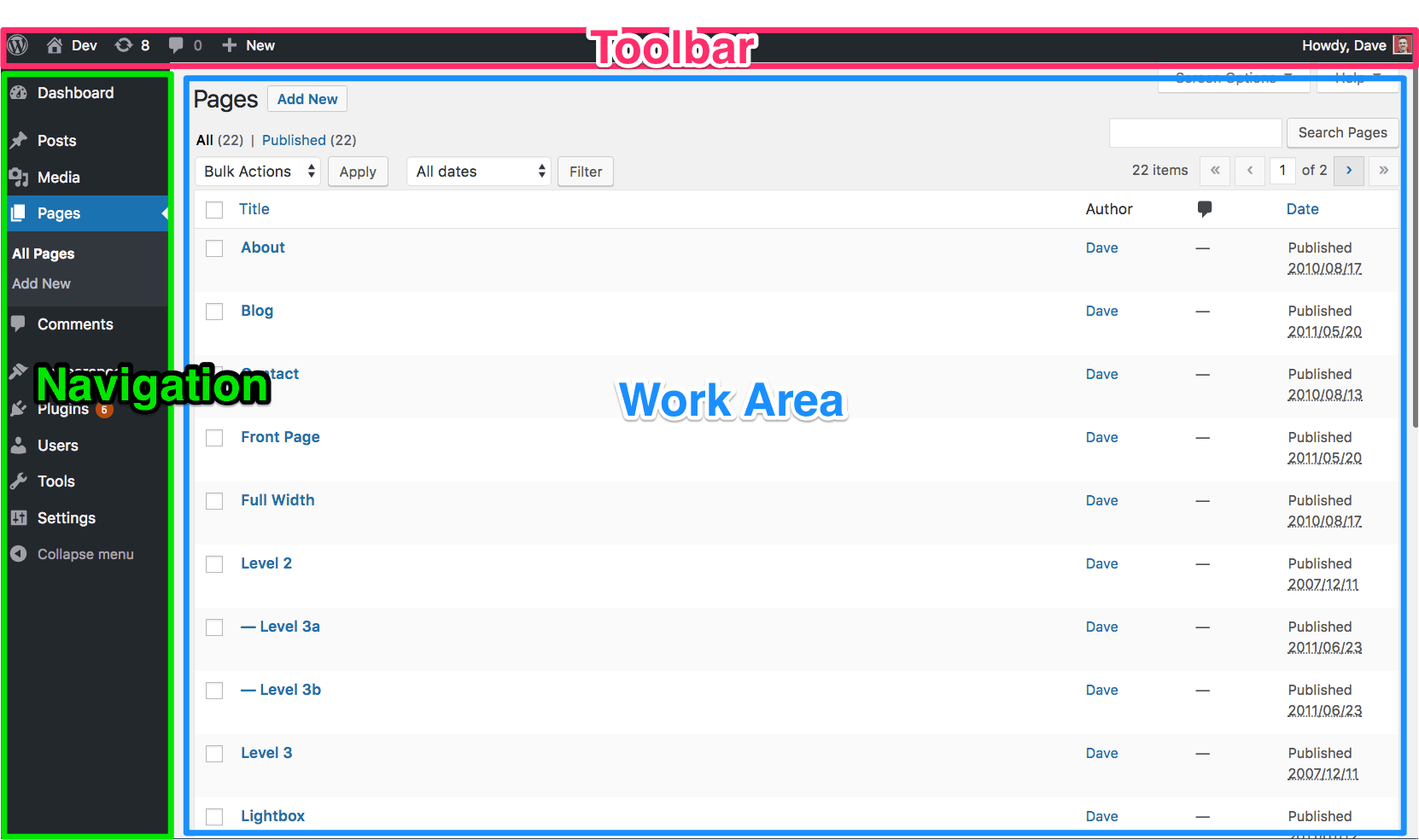
Toolbar at the top
The Toolbar (previously called the Admin Bar) is the dark grey bar at the top of the screen. On the left-hand side, it contains links to commonly used administrative functions, such as:
- Visit your site
- View comments
- Updates that are available
- Create a new post, page or user
On the right-hand side, you’ll find links to:
- Edit your profile
- Logout
By default, you will also see the WordPress Toolbar when viewing your actual website. You can turn this off by updating a setting on your profile.
Navigation on the left
The main navigation provides quick access to all administrative screens in the admin area. You will use this to jump between different administrative pages. We’ll take a closer look in the next section.
Work Area everywhere else
This area is where you will actually make & save your changes. The content you see in this area will depend on which administration screen you are currently viewing. Some examples include:
- Edit site settings
- Install/Activate/Update plugins & themes
- Upload images & other media
- Create/Edit posts, pages & other content
- …and much more
Now that you’re acquainted, let’s talk about each section within the main navigation, and what types of actions you can perform.
Navigating the Admin Area
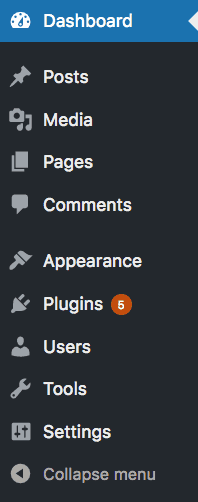
There are 10 main sections in the admin area, each with sub-sections beneath them.
- Dashboard
- Posts
- Media
- Pages
- Comments
- Appearance
- Plugins
- Users
- Tools
- Settings
Let’s briefly discuss each section and what you can accomplish with it.
Dashboard
There’s nothing to actually edit on your Dashboard. It’s purpose is to:
- Show you recent activity on your site
- Provide links to commonly used administrative tasks
- Keep you up-to-date on WordPress news & events
WordPress plugins can also add information to your Dashboard, making it even more useful for your particular site.
Posts
This is where you create, edit & delete blog posts, as well as manage your post’s categories & tags. Posts differ from Pages in that they are usually time-sensitive, and contain categories and/or tags to organize them. We’ll talk about Pages in just a second.
Media
The Media section is where you upload images, PDFs and other media files. Media files can be uploaded via numerous pages in the admin area, but this section is where you will manage them (delete, edit alt text, etc.).
Pages
Pages are similar to posts, as they also represent content that you can add to your site. However, unlike Posts, they are not time-sensitive, nor are they organized into categories and/or tags.
You will create, edit, delete and manage all of your sites static content in this section.
Comments
The Comments section is exactly what you’d expect; it’s where you manage blog comments left by your site’s visitors. You can add replies, delete and even edit comments from this screen.
Regardless of whether you have comments turned on or off, you will always see this section in your WordPress admin area.
Appearance
Under Appearance, there are several sub-sections that each serve a different purpose.
- Themes is where you can add, delete and choose the active theme you want to control the design of your WordPress site.
- Customize takes you to the WordPress Customizer. This is where you can edit many aspects of your theme, and test out the changes before making them live.
- Widgets are pieces of content that you can add to WordPress sidebars. Depending on your theme, you could have multiple sidebars located in different areas of your site.
- Menus provide an easy way for you to create & manage a list of links on your site, commonly referred to as a “menu,” or “navigation.”
Plugins
Plugins provide additional functionality to your WordPress site. There are two main screens in the Plugins section:
- Installed Plugins displays a list of your current plugins, and allows you to activate/deactivate, update and delete them
- Add New is where you search for and install new plugins
Users
Users are the people who have access to the WordPress admin area. There are a few different roles that a user can be assigned, depending on what level of responsibility they should have when editing your site.
In this section, you can:
- Edit your own user profile
- Add new users or delete existing ones
- Manage other user’s profiles
Tools
In the Tools section, you can import & export your WordPress content, as well as convert categories to tags (and vice versa). These are seldomly used features, but could prove useful if you’re making sweeping changes to your site.
Settings
This is where you can edit a handful of settings that impact your site as a whole. They are broken down into a few sub-sections:
- General settings include your site title, URL, email address, time zone & language
- Writing settings include a default post category & post format
- Reading settings include homepage & blog post display options, as well as search engine visibility
- Discussion settings all relate to how comments will appear on your site
- Media settings include a few image size choices, as well as how you want to organize the uploads on your server
- Permalink settings determine the format of your URLs
That covers the primary sections of the WordPress admin area, and what each of them are used for.